Siamese Tracking of Cell Behaviour Patterns
Abstract
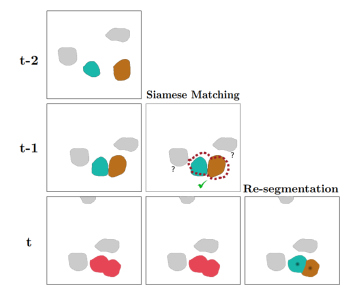
Tracking and segmentation of biological cells in video sequences is a challenging problem, especially due to the similarity of the cells and high levels of inherent noise. Most machine learning-based approaches lack robustness and suffer from sensitivity to less prominent events such as mitosis, apoptosis and cell collisions. Due to the large variance in medical image characteristics, most approaches are dataset-specific and do not generalise well on other datasets. In this paper, we propose a simple end-to-end cascade neural architecture that can effectively model the movement behaviour of biological cells and predict collision and mitosis events. Our approach uses U-Net for an initial segmentation which is then improved through processing by a siamese tracker capable of matching each cell along the temporal axis. By facilitating the re-segmentation of collided and mitotic cells, our method demonstrates its capability to handle volatile trajectories and unpredictable cell locations while being invariant to cell morphology. We demonstrate that our tracking approach achieves state-of-the-art results on PhC-C2DL-PSC and Fluo-N2DH-SIM+ datasets and ranks second on the DIC-C2DH-HeLa dataset of the cell tracking challenge benchmarks.