 | Content-Based Video Retrieval: Three Example Systems from TRECVid In International Journal of Imaging Science and Technology 2008. [bibtex] [pdf] [url] |
Abstract
The growth in available online video material over the
Internet is generally combined with user-assigned tags or content
description, which is the mechanism by which we then access such
video. However, user-assigned tags have limitations for retrieval and often
we want access where the content of the video itself is directly
matched against a userís query rather than against some manually
assigned surrogate tag. Content-based video retrieval techniques are
not yet scalable enough to allow interactive searching on Internet-scale,
but the techniques are proving robust and effective for smaller collections.
In this article, we show three exemplar systems which demonstrate
the state of the art in interactive, content-based retrieval of video
shots, and these three are just three of the more than 20 systems developed
for the 2007 iteration of the annual TRECVid benchmarking activity.
The contribution of our article is to show that retrieving from video
using content-based methods is now viable, that it works, and that
there are many systems which now do this, such as the three outlined
herein. These systems, and others can provide effective search on hundreds
of hours of video content and are samples of the kind of contentbased
search functionality we can expect to see on larger video archives
when issues of scale are addressed.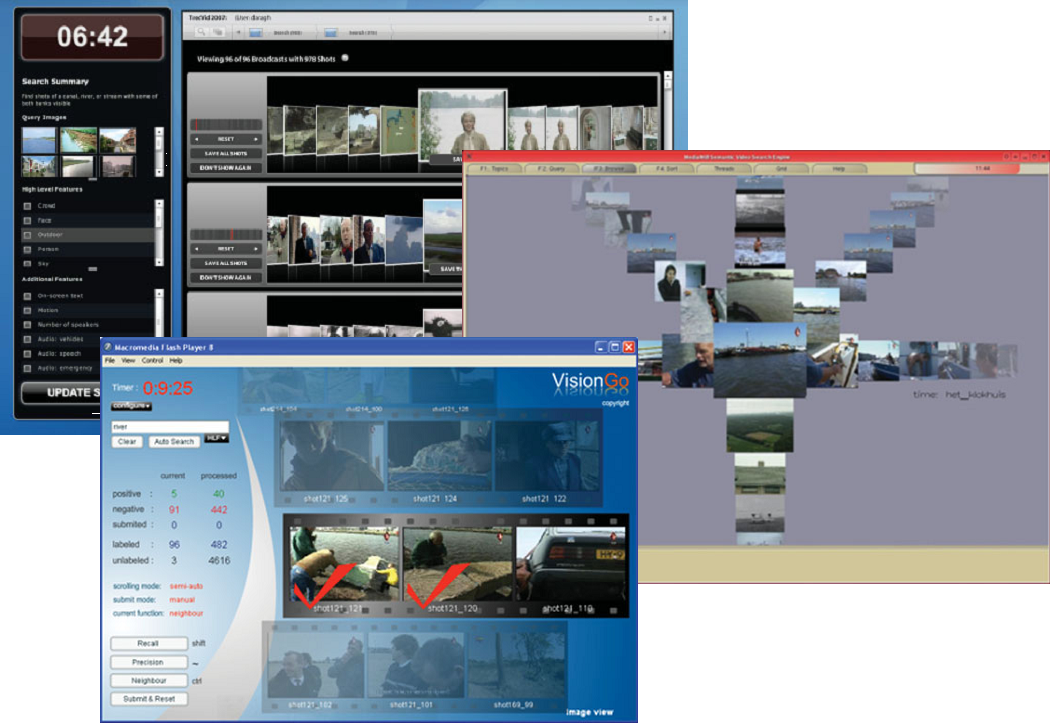
Bibtex Entry
@Article{SmeatonIJIST2008,
author = "Smeaton, A. F. and Wilkins, P. and Worring, M. and de Rooij, O.",
title = "Content-Based Video Retrieval: Three Example Systems from TRECVid",
journal = "International Journal of Imaging Science and Technology",
number = "2-3",
volume = "18",
pages = "195--201",
year = "2008",
url = "https://ivi.fnwi.uva.nl/isis/publications/2008/SmeatonIJIST2008",
pdf = "https://ivi.fnwi.uva.nl/isis/publications/2008/SmeatonIJIST2008/SmeatonIJIST2008.pdf",
has_image = 1
}