 | Color Constancy by Derivative-Based Gamut Mapping In ICCV Workshop on Photometric Analysis for Computer Vision 2007. [bibtex] [pdf] [url] |
Abstract
Color constancy aims to compute object colors despite
differences in the color of the light source. Gamut-based
approaches are very promising methods to achieve color
constancy. In this paper, the gamut mapping approach is
extended to incorporate higher-order statistics (derivatives)
to estimate the illuminant.
A major problem of gamut mapping is that in case of
a failure of the diagonal model no solutions are found,
and therefore no illuminant estimation is performed. Image
value offsets are often used to model deviations from
the diagonal model. Prior work which incorporated robustness
to offsets for gamut mapping assumed a constant offset
over the whole image. In contrast to previous work, we
model these offsets to be position dependent, and show that
for this case derivative-based gamut mapping yields a valid
solution to the illuminant estimation problem.
Experiments on both synthetic data and images taken under
controlled laboratory settings reveal that the derivativebased
and regular gamut mapping methods provide similar
performance. However, the derivative-based method outperforms
other methods on the more challenging task of
color constancy for real-world images.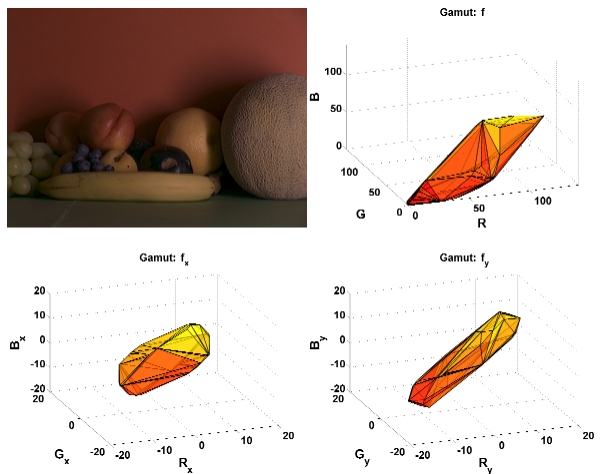
Info
http://www.science.uva.nl/~gijsenijSee also this paper
www.colorconstancy.com
Bibtex Entry
@InProceedings{GijsenijPACV2007,
author = "Gijsenij, A. and Gevers, T. and van de Weijer, J.",
title = "Color Constancy by Derivative-Based Gamut Mapping",
booktitle = "ICCV Workshop on Photometric Analysis for Computer Vision",
year = "2007",
url = "https://ivi.fnwi.uva.nl/isis/publications/2007/GijsenijPACV2007",
pdf = "https://ivi.fnwi.uva.nl/isis/publications/2007/GijsenijPACV2007/GijsenijPACV2007.pdf",
has_image = 1
}