 | Physics-Based Edge Evaluation for Improved Color Constancy In IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2009. [bibtex] [pdf] [url] |
Abstract
Edge-based color constancy makes use of image derivatives
to estimate the illuminant. However, different edge
types exist in real-world images such as shadow, geometry,
material and highlight edges. These different edge types
may have a distinctive inf luence on the performance of the
illuminant estimation.
Therefore, in this paper, an extensive analysis is provided
of different edge types on the performance of edge-based
color constancy methods. First, an edge-based taxonomy is
presented classifying edge types based on their ref lectance
properties (e.g. material, shadow-geometry and highlights).
Then, a performance evaluation of edge-based color constancy
is provided using these different edge types. From
this performance evaluation, it is derived that certain edge
types are more valuable than material edges for the estimation of the illuminant. To this end, the weighted Grey-Edge
algorithm is proposed in which certain valuable edge types
are more emphasized for the estimation of the illuminant.
From the experimental results, it is shown that the proposed
weighted Grey-Edge algorithm based on the shadowshading
variant, i.e. assigning higher weights to edges
with more energy in the shadow-shading direction, results
in the best performance. Moreover, all current state-of-theart
methods, including pixel-based methods and edge-based
methods, have been signif icantly outperformed by the proposed
weighted Grey-Edge algorithm, resulting in an improvement
of 9% over the current best-performing algorithm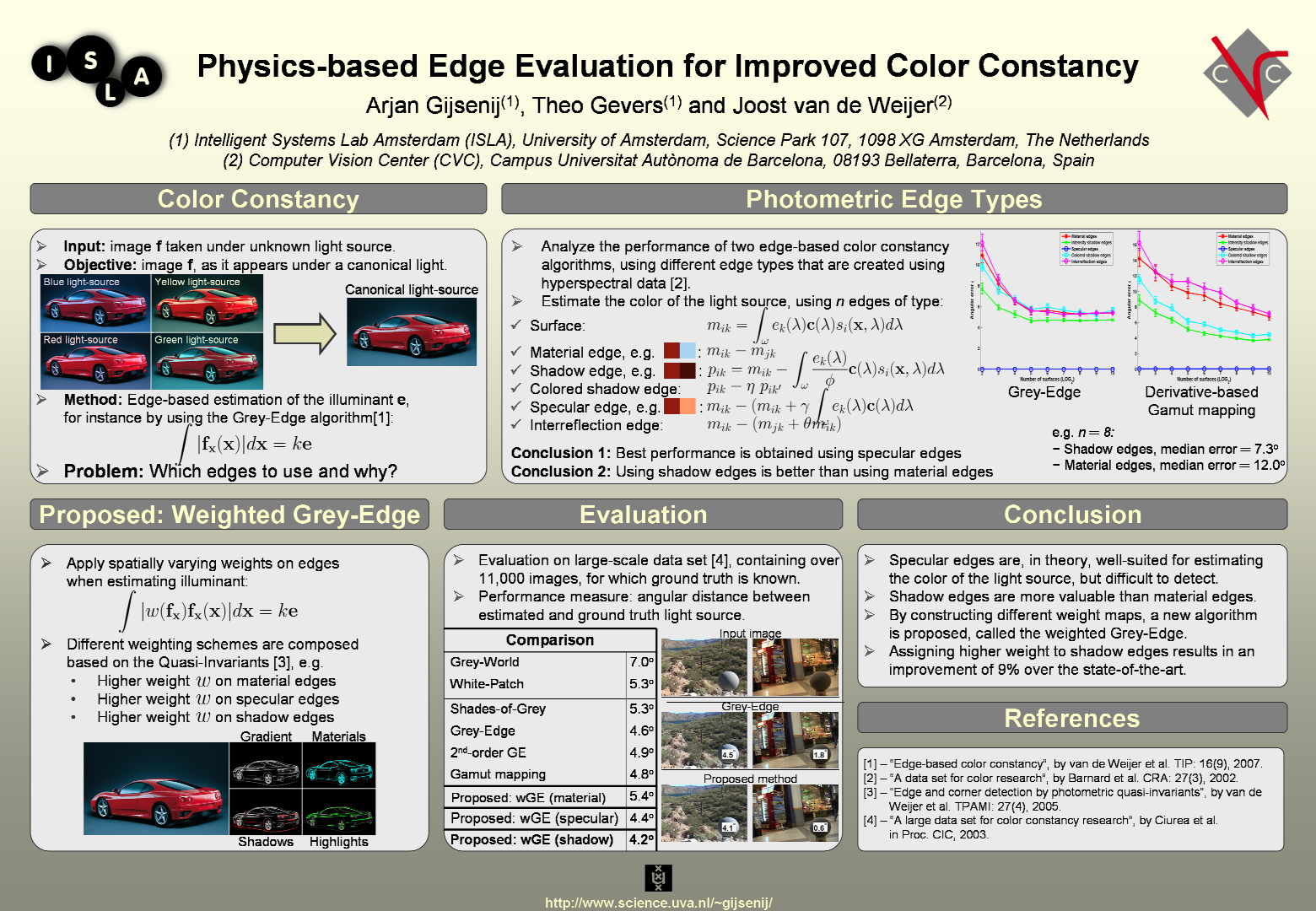
Info
http://www.science.uva.nl/~gijsenijwww.colorconstancy.com
Bibtex Entry
@InProceedings{GijsenijCVPR2009,
author = "Gijsenij, A. and Gevers, T. and van de Weijer, J.",
title = "Physics-Based Edge Evaluation for Improved Color Constancy",
booktitle = "IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition",
year = "2009",
url = "https://ivi.fnwi.uva.nl/isis/publications/2009/GijsenijCVPR2009",
pdf = "https://ivi.fnwi.uva.nl/isis/publications/2009/GijsenijCVPR2009/GijsenijCVPR2009.pdf",
has_image = 1
}