 | Eyes Do Not Lie: Spontaneous Versus Posed Smiles In ACM International Conference on Multimedia 2010. [bibtex] [pdf] [url] |
Abstract
Automatic detection of spontaneous versus posed facial expressions
received a lot of attention in recent years. However,
almost all published work in this area use complex
facial features or multiple modalities, such as head pose and
body movements with facial features. Besides, the results
of these studies are not given on public databases. In this
paper, we focus on eyelid movements to classify spontaneous
versus posed smiles and propose distance-based and angular
features for eyelid movements. We assess the reliability of
these features with continuous HMM, k-NN and naĻıve Bayes
classifiers on two different public datasets. Experimentation
shows that our system provides classification rates up to 91
per cent for posed smiles and up to 80 per cent for spontaneous
smiles by using only eyelid movements. We additionally
compare the discrimination power of movement features
from different facial regions for the same task.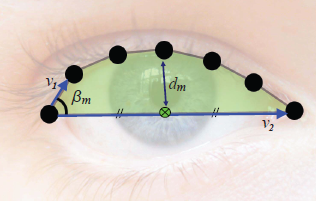
Bibtex Entry
@InProceedings{DibekliogluICM2010,
author = "Dibeklioglu, H. and Valenti, R. and Salah, A. A. and Gevers, T.",
title = "Eyes Do Not Lie: Spontaneous Versus Posed Smiles",
booktitle = "ACM International Conference on Multimedia",
year = "2010",
url = "https://ivi.fnwi.uva.nl/isis/publications/2010/DibekliogluICM2010",
pdf = "https://ivi.fnwi.uva.nl/isis/publications/2010/DibekliogluICM2010/DibekliogluICM2010.pdf",
has_image = 1
}